
Imagine you’re closing Q4 books and find 30 unmatched transactions…
Incorrect financial reporting can have significant consequences for companies and all their stakeholders, such as investors and shareholders. Therefore, it’s essential for every company to monitor both income and expenditure. In this way, a company can ensure operational efficiency, make more accurate decisions, and improve control over its financial affairs.
To ensure your financial reporting is accurate and healthy, you must set up a robust payment reconciliation that can leverage AI technology. According to Modern Treasury’s 2025 report, 94% of financial leaders expressed excitement about automating workflows, and 76% of software-focused companies actually decided to invest in payment automation.
In this blog, we’ll explain the meaning of payment reconciliation, how the payment reconciliation process works, and how modern technology can help automate and accelerate parts of it. Let’s get started!
Key Takeaways
- Payment reconciliation is the process of ensuring that payments recorded in your financial systems match actual transactions from bank statements, invoices, and receipts, being crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance.
- The ROI of payment reconciliation automation is significant: reduced labor costs, faster month-end closing, improved accuracy, real-time insights, and scalability without increasing headcount.
- Before automating, organizations should consider factors like system compatibility, budget, and technical expertise and choose solutions that integrate easily into existing finance ecosystems.
- Solutions like Klippa’s SpendControl make it easy to automate reconciliation workflows, prevent fraud, and integrate with your ERP, empowering your finance team to focus on strategic decisions.
What is Payment Reconciliation?
Payment reconciliation is the process of matching up a payment received with the corresponding invoices, receipts, or other documents, ensuring that the payment is properly applied. In essence, it ensures that payments and bank statements align with an organization’s accounting records, keeping financial data accurate and up-to-date for processes like month-end and year-end closing.
For example, when an organization receives a financial statement, such as a bank statement, costs and payments are compared against invoices or receipts to ensure the accuracy of accounts payable or accounts receivable on the balance sheet.
How Does Payment Reconciliation Work?
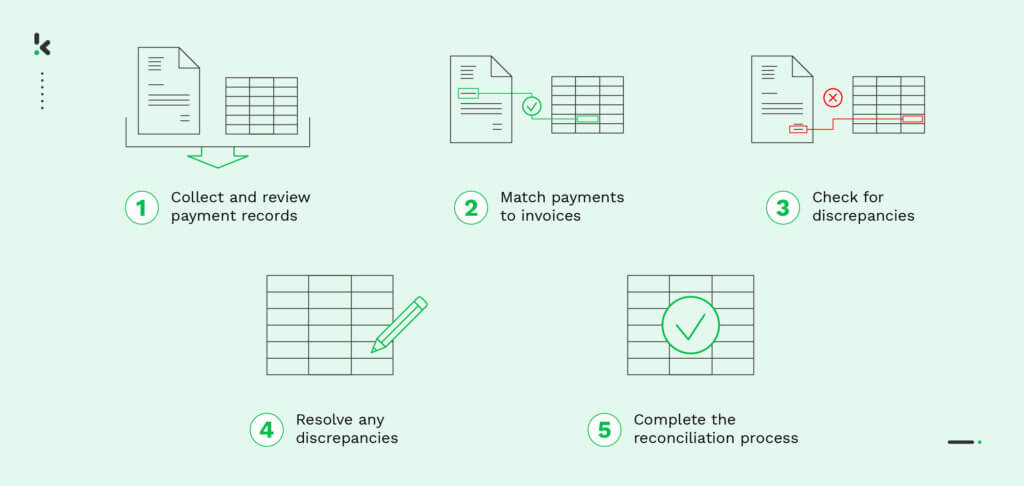
The payment reconciliation process can vary depending on the organization, its systems, and the specific payment circumstances. However, the following steps are often involved in the reconciliation process:
- Collect and review payment records: The first step is to gather all relevant payment records, such as invoices, receipts, and bank statements, and review them to ensure they are complete and correct for the respective time period.
- Match payments to invoices: The next step is to match payments to corresponding invoices or receipts. This can be done by checking the payment amount, payment dates, and payee information from the bank statement.
- Check for discrepancies: After payments have been matched to invoices, it is important to check for discrepancies or errors to ensure that all payments are accounted for.
- Resolve any discrepancies: If any discrepancies are found during the reconciliation process, they should be addressed and resolved. This may involve contacting the suppliers or vendors to clarify payment details or simply adjusting the financial records if needed.
- Complete the reconciliation process: Once all payments have been reconciled, the process is considered complete. Often, it is needed to prepare reports or summaries of the reconciled payments.

As addressed before, all of the previously mentioned steps are not always mandatory, and some organizations may have more or fewer steps in their payment reconciliation processes.
For small firms, the process can be very straightforward with fewer clients, vendors, and cash flows compared to the bigger ones. However, when an organization scales, a workflow like the accounts payable process quickly becomes labor-intensive, increasing the complexity and risks of error. This can lead to various drawbacks, which are discussed below.
Challenges of Payment Reconciliation
With the modern landscape of different payment methods and evolving financial technologies, businesses face several challenges when reconciling payments, ranging from regulatory compliance to data fragmentation and cybersecurity concerns.
If the payment reconciliation process is performed manually, there are even more drawbacks encountered, such as:
- Inaccurate data: With a high chance of human error, mistakes are bound to happen, which will lead to discrepancies in data that can be challenging to resolve.
- Time-consuming: Companies can waste a significant amount of time reconciling payments, especially when it’s done manually or if there are many payments to reconcile.
- Inefficiency: Many traditional payment reconciliation processes rely on manual data entry and manual matching of payments and invoices, which can be extremely inefficient and prone to errors.
- Lack of visibility: With the traditional process, companies don’t have a real-time overview of their expenses, payments, and outstanding invoices. The lack of cash flow oversight can be challenging for businesses to make informed decisions.
- Risk of fraud: Any individual can create fake invoices or alter real invoices to receive payment for goods or services that were not provided using fictional company details. This is also known as invoice fraud.
Manual vs. Automated: What’s the Real ROI?
Let’s be honest: when you think about optimizing financial operations, you often overlook payment reconciliation processes, even though they’re so time-consuming and prone to errors.
Traditional manual reconciliation involves collecting data from multiple sources, matching transactions, and resolving mismatches through emails or phone calls. On the other hand, automated reconciliation makes use of AI, machine learning, and systems integration to pull in the data from feeds, invoices, and ERPs, automatically matching payments to records, flagging discrepancies, and even suggesting resolutions.
Let’s break this down with a practical example.
Consider a mid-sized company handling 2.000 transactions per month across multiple bank accounts, platforms, and vendors.
What would a month of payment reconciliations look like with manual and automated workflows?
| Category | Manual reconciliation | Automated reconciliation |
| Average transactions/month | 2.000 | 2.000 |
| Time per transaction | 5–7 minutes | Instant for ~95%, manual review only for exceptions |
| Total Time Required | 167–233 hours/month (≈4 – 6 weeks) | 10–15 hours/month |
| Labor Cost (@€35/hour) | €7,000+ | ~€500 |
| Error Risk | High (manual matching, delayed detection) | Low (real-time alerts, automatic matching) |
| Month-End Closing Time | Often delayed | Up to 50% faster |
| Scalability | Limited (linear cost with volume) | High (handles growth without additional headcount) |
| Real-Time Insights | Not available | Full visibility into financial status |
Now, it’s so much easier to see the actual ROI of automating payment reconciliation: lower costs, faster processing, improved accuracy, and reduced risk. But, at the same time, it’s important to recognize that not all reconciliation workflows are created equal.
Since the complexity and the structure of your process often depend on the type of payments your business handles, understanding these variations is a key step in designing an automation strategy that fits you.
Let’s take a closer look at the most common types of payment reconciliation.
Common Types of Payment Reconciliation
As businesses navigate a diverse array of payment methods, from traditional banking channels to emerging fintech solutions and cryptocurrencies, the process of reconciling payments becomes increasingly complex.
Here are the most common types of payment reconciliation:
- Bank Reconciliation. Most reconciliations are primarily about matching transactions recorded in a company’s financial records with those listed on bank statements, ensuring accuracy in financial reporting.
- Invoice Reconciliation. Invoice reconciliation involves comparing the transactions recorded in a company’s financial records. This process ensures accuracy in financial reporting and helps identify discrepancies or errors in invoicing.
- Cash Reconciliation. Cash reconciliation entails verifying the cash transactions recorded in a company’s financial records with the actual cash on hand or in the company’s bank accounts. This process ensures accuracy in financial reporting and helps identify any discrepancies or errors.
- Credit Card Reconciliation. Both customers and businesses use credit cards as a means of payment for their purchases. Credit card reconciliation involves verifying transactions made using credit cards by comparing them with monthly credit card statements and internal financial records.
- Online Payment Service Reconciliation. Reconciling transactions processed through platforms like Venmo or PayPal entails aligning payment records with corresponding bank statements and internal financial records.
- Vendor Payment Reconciliation. Vendor reconciliation involves comparing the transactions recorded in a company’s financial records with the invoices and payments made to vendors or suppliers. This process ensures accuracy in financial reporting and helps identify any discrepancies or errors in vendor transactions.
- Cryptocurrency Reconciliation. With the emergence of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, reconciling transactions involving digital currencies requires tracking and matching transactions on blockchain ledgers, adding another layer of complexity to the reconciliation process.
Each of these reconciliation types plays a critical role in maintaining financial accuracy, but they also come with their own unique challenges. That’s why adopting standardized practices will make such a big difference.
Here are two best practices to help your reconciliation process run smoothly and more efficiently.
Best Practices for Your Company’s Reconciliation Process
Accurate financial records are vital for business success. However, with the complexity of payment methods, regulations, and cybersecurity risks, reconciliation can be challenging. Adopting best practices can streamline this process. Two key practices are:
Regular Reconciliation Dates
Set consistent dates for reconciling financial records, either on a weekly or monthly basis. This ensures that reconciliation tasks are performed regularly and helps prevent backlogs or delays. Additionally, scheduling regular reconciliation dates promotes accountability within your finance team and facilitates timely decision-making based on up-to-date financial information.
Use Automated Reconciliation Software
Manual reconciliation processes are time-consuming, prone to errors, and often inefficient, especially as transaction volumes increase. Implementing automated reconciliation software speeds up the process, reduces errors, and frees up time for more strategic tasks.
Benefits of Automated Payment Reconciliation Software
Automated payment reconciliation is a transformative tool for businesses, revolutionizing how financial transactions are managed, recorded, and reconciled. Here are the key benefits that highlight why incorporating automated payment reconciliation into your business operations is not just a smart move but a necessary one:
Time Efficiency
Automated payment reconciliation streamlines the laborious task of matching bank statements with invoices, saving significant time. Instantly comparing and reconciling transactions against records frees up the finance team to concentrate on strategic duties instead of manual data entry.
Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Manual reconciliation is prone to human error, which can lead to discrepancies and financial inaccuracies. Automated systems minimize these risks by ensuring that transactions are matched accurately, reducing the likelihood of mistakes that could lead to financial discrepancies.
Real-Time Financial Insight
With automated reconciliation, you gain access to real-time financial data, providing an up-to-date overview of your financial status. This immediate insight is crucial for making informed business decisions, managing cash flow effectively, and identifying financial trends or irregularities quickly.
Fraud Detection and Enhanced Security
Automated reconciliation software often comes with built-in security features that help detect fraudulent transactions and discrepancies. By continuously monitoring transactions, these systems can alert you to unusual activity, helping to protect your business from potential fraud.
Improved Compliance and Audit Readiness
Maintaining compliance with financial regulations is easier with automated reconciliation. These systems keep a detailed, timestamped log of all transactions and reconciliations, making it simpler to demonstrate compliance during audits and reducing the stress and workload associated with audit preparations.
Cost Savings
By automating the reconciliation process, businesses can reduce the need for additional staff to manage financial transactions, leading to significant cost savings. Additionally, the reduction in errors and fraud also contributes to financial savings in the long run.
Enhanced Stakeholder Satisfaction
Automating payment reconciliation streamlines the payment process for both suppliers and customers, leading to faster payment cycles and improved relationships. This efficiency can enhance your business’s reputation and lead to more favorable terms and conditions with suppliers.
Scalability
As your business grows, the volume of transactions is likely to increase. Automated reconciliation systems can scale with your business, handling an increasing number of transactions without the need for additional resources or a decrease in performance.
Automating payment reconciliation enhances financial transaction management by ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and security. By embracing technology for this critical process, businesses improve financial health, compliance, and operational efficiency.
What to Consider When Switching to Automated Payment Reconciliation
There are a few factors that can make it challenging for your business to automate the payment reconciliation process. The following section discusses these challenges and tips for overcoming them.
Change of the existing systems
If your organization is large and is operating with complex systems, it can be difficult to implement software to automate payment reconciliation due to the possible need to change the existing system.
Find out if the solution offers the right integration possibilities via a consultation call or online demonstration with the solution provider (it’s free!).
Limited resources
Automating the payment reconciliation process may require investment in new software or other resources, which can be a challenge if you have limited resources.
Think about the long-term financial benefits that the solution may provide by calculating the ROI based on time and costs. If it costs less or at least the same amount as it would with manual payment reconciliation workflow, then it is definitely worth implementing.
Lack of technical expertise
Businesses may struggle with automation if they do not have the necessary technical expertise in-house or if they are not familiar with the software or systems that are needed to automate the process.
In such a case, make sure that the solution provider can help with customer onboarding and implementation, or simply acquire a low-code solution that would not require technical expertise.
Even potential challenges can be overcome as the benefits of switching to automated payment reconciliation still outweigh the risks.
For example, Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG), a leading financial institution from Japan, now enjoys fully digital expense and invoice processing, greater financial control and accuracy, seamless ERP integration, and reduced administrative workload.
Would you like the same for your business? In the next section, we will present a possible solution to start your journey to automation.
Automate Your Payment Reconciliation Process with Klippa

Software solutions like Klippa SpendControl integrate both technologies to automate expense management and invoice processing workflows, including payment reconciliation. With SpendControl, you can empower your financial and accounting departments by enabling them to:
- Easily submit and approve receipts and invoices via the mobile app or web application
- Automatically record expenses directly in the accounting system with self-learning journal entries, eliminating manual data entry
- Prevent fraud with automatic detection of duplicate claims
- Conveniently integrate the solution to any accounting and ERP software without the need to change everything entirely
- Reconcile payments automatically with intelligent two-way matching
Are you ready to streamline your company’s payment reconciliation process and devote more time to your core values? Schedule a free demo with our SpendControl Experts today!
FAQ
Regular payment reconciliation helps detect errors, prevent fraud, ensure accurate financial reporting, and maintain compliance with financial regulations.
Common challenges include data entry errors, timing differences between recorded transactions and bank postings, missing or duplicate transactions, and unauthorized or fraudulent activities.
Klippa offers a pre-accounting solution that processes expenses, invoices, and credit card transactions, sending submitted data to authorized personnel and automating approvals based on smart business rules.
Yes, Klippa supports international payment reconciliation, accommodating multiple currencies and compliance with international financial regulations.
Klippa employs robust security protocols, including data encryption and compliance with GDPR, to ensure the protection of sensitive financial information.