
Document fraud is a persistent threat that can severely impact your business. From potential financial losses to reputational damage and exhausting legal battles, the stakes are too high. In the U.S. alone, a staggering 2.6 million fraud cases were reported last year, making it clear that no business is immune, including yours. Fraud isn’t something you can leave to chance.
Fortunately, smart fraud detection technologies are available, making it easier for you to remain proactive and keep your business out of harm’s way. In this blog, we will explain what document fraud entails, discuss the most common types, and highlight some of the best technologies you can harness for seamless fraud detection within your document workflows. Let’s go!
Key Takeaways
- Document fraud is more common than you think – and it can cost your business time, money, and trust.
- Manually checking documents isn’t enough anymore. Automated tools catch fraud faster and with way fewer errors.
- With smart tech like OCR, AI, and checks for duplicates or image edits, fraud can be spotted before it slips through.
- Tools like Klippa DocHorizon make fraud detection easy, helping you stay secure and compliant without slowing down your workflow.
What is Document Fraud?
Document fraud refers to the creation, alteration, or use of falsified or illegitimate documents to deceive, defraud, or pass through various checks. These can range from minor alterations on ID cards to falsifying financial records or academic credentials.
Document fraud can be used for various illegal purposes, including identity theft or facilitating illegal activities such as human trafficking and terrorism. What does this mean for you? With document fraud at large, you’re always at risk of great financial losses, damage to the integrity of your business, security breaches, and non-compliance with industry regulations (like KYC and AML rules).
To tackle document fraud, first, you need to know the different kinds of document fraud you can encounter and the effect they can have on your business. And that’s what our next section is about.
Common Types of Document Fraud
Here are some of the most common types of document fraud:
Identity Fraud
This involves using altered, fake, or stolen identity documents to commit identity theft or bypass age verification policies. This fraud can cause your business financial and reputational damage due to the fraudulent transactions, as well as legal repercussions for providing 18+ products or services to minors.
Invoice Fraud
Invoice fraud involves submitting fraudulent, altered, or duplicate invoices for unlawful financial gain, often due to vendor fraud, expense fraud, or human error. It poses financial and non-compliance risks and breaches trust within your company and with partners.
Receipt Fraud
This type of fraud involves manipulating, fabricating, or submitting duplicate receipts. The risks include illegitimate expense reimbursements and unwarranted cashback or loyalty point payouts, impacting your bottom line.
Loan or Mortgage Fraud
Loan or mortgage fraud involves the submission of falsified documents, including fake bank statements, tax returns, or property appraisals, to obtain loans or mortgages. This risks financial losses for you as a lender and compliance concerns.
Insurance Fraud
This can range from falsifying information on application forms to exaggerating claims to receive payouts fraudulently. Individuals can submit fake documents, like fake medical records or inflated property damage claims, to receive undeserved insurance payouts, risking financial losses for the insurance industry.
- Loyalty Fraud: From fake receipts to fake coupons, loyalty fraud refers to the creation and submission of altered receipts or coupons by fraudsters intended to obtain benefits to which they are not entitled. Not only will it result in financial damage for your business, but it can also damage your brand reputation and consumer trust.
As you can see, there are so many possibilities for fraud to take place across a range of industries. Let’s see how you can safeguard yourself from it!
How to Detect Fraudulent Documents with Automation?
When it comes to document fraud detection, you have two options: doing it manually or with the help of an automated document verification solution. While doing it by hand may seem like a good idea at first, fraud is getting more advanced every year, and human eyes can miss those subtle inconsistencies, especially when reviewing large volumes. Plus, can you really afford the time it takes to verify each document manually?
The alternative is Intelligent Document Processing (IDP). Equipped with OCR (Optical Character Recognition) and Artificial Intelligence, IDP is capable of spotting fraud and suspicious patterns in documents in real time. With this technology, you have your best chance to catch fraud before it slips through the cracks. In this section, we’ll show you how IDP makes it possible!
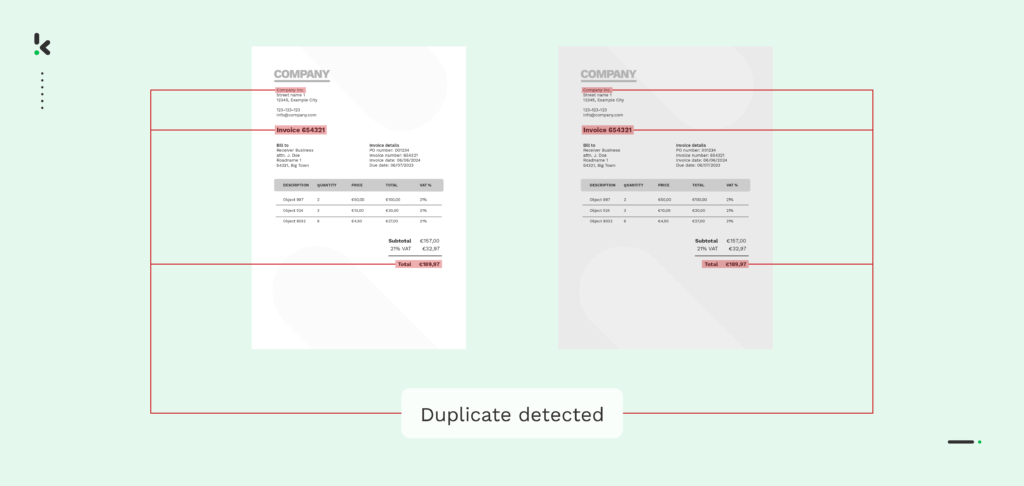
Duplicate Detection
Duplicate detection is an essential step in preventing duplicate payments or double bookings, especially when it comes to reimbursing expenses, tackling spend management tasks, or receipt clearing in loyalty campaigns. With duplicate detection, each document processed is given a distinct digital fingerprint called “hash”, making it easier to detect when a duplicate has been uploaded.
For example, in the case of invoice processing, the software assigns each invoice a unique hash based on its structure, invoice number, merchant name, purchase date, and amount. If an invoice with the same details is uploaded again, it’s flagged as a duplicate, and you’re notified. This can also be applied to receipts, CVs, coupons, and other document types.

Photoshop Detection
Photoshop Detection refers to different technologies identifying whether a submitted document has been digitally altered using software like Adobe Photoshop. It involves analyzing metadata, lighting, shadows, or textures not typically present in unedited photos.
Copy-move detection
Copy-move detection is like a digital detective tool for images. It hunts down areas in pictures that have been copied or changed. Copy-move detection enables IDP to analyze the documents by studying patterns and similarities. It picks up on the signs of image manipulation or fakery, flagging any suspicious sections that appear identical or altered.
Imagine yourself as a bank employee reviewing bank statements for mortgage applications. If someone tried to forge a signature by copying and pasting it onto another document, this technique would spot the duplicated signature, enabling you to decline such fraudulent loan applications instantly.
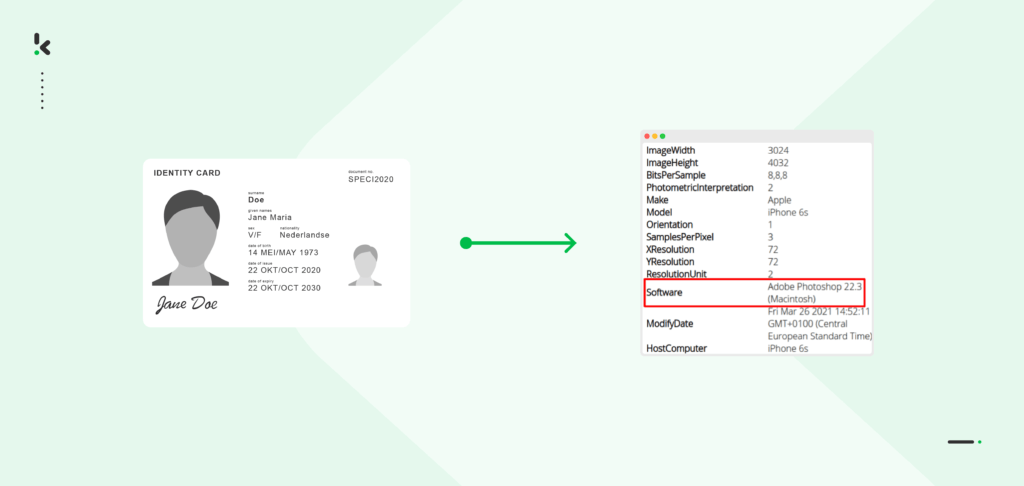
EXIF analysis
EXIF data analysis examines the metadata within digital images or PDFs to verify document authenticity. Metadata outlines basic information about a file, such as author type, creation date, usage, file size, and more. EXIF data analysis scrutinizes this metadata to analyze the creation/modification timestamps, device information, and GPS coordinates.
For example, you are a back office employee reviewing receipts submitted for a loyalty campaign. If someone has tried to alter the details on the receipt (eg, total amount, purchase date) with software like Photoshop, EXIF data analysis will indicate the presence of the software, which could indicate tampering and photo editing. It’s a valuable tool in document fraud detection, providing insights into digital document origins and integrity.

Grayscale analysis
Grayscale analysis is a method used to analyze the intensity levels of pixels in grayscale images. This involves examining the distribution of pixel values across the image, typically ranging from black to white.
For example, you are a hiring manager presented with academic credentials for a prospective employee and you need to verify the qualifications of this applicant through these credentials. Grayscale analysis would help you spot any changes to the pixel intensity. Did the candidate manipulate text, signatures, or logos? Greyscale analysis helps you spot that much easier and verify the authenticity of the document.
Cross-validation
Cross-validation techniques are those that involve verifying the authenticity and integrity of a document by comparing multiple document fields or sources of information to corroborate a document’s validity.
MRZ Verification
MRZ (Machine Readable Zone) verification is a method used to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the data encoded in the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) of identity and travel documents such as passports, visas, and ID cards. This process involves checking the digits, which are calculated and embedded within the MRZ to allow for error detection.
For example, a fraudster might attempt to alter a document without considering the complexities of the MRZ. During identity verification, the software checks the MRZ data by calculating and validating checksums. If the checksums do not match the data on the document, the document is flagged as suspicious.
Data Matching
Data matching refers to the process of comparing data from a document against trusted or already verified data sources to identify inconsistencies, discrepancies, or fraudulent entries. This technique helps validate the authenticity of the document by ensuring that the information it contains aligns with known and accurate data.
For example, when reviewing a new bank account application with a utility bill as proof of address, cross-document validation involves comparing details like name and address with other documents like identity documents, payslips, or employment contracts. Discrepancies, such as different addresses, could indicate potential fraud.
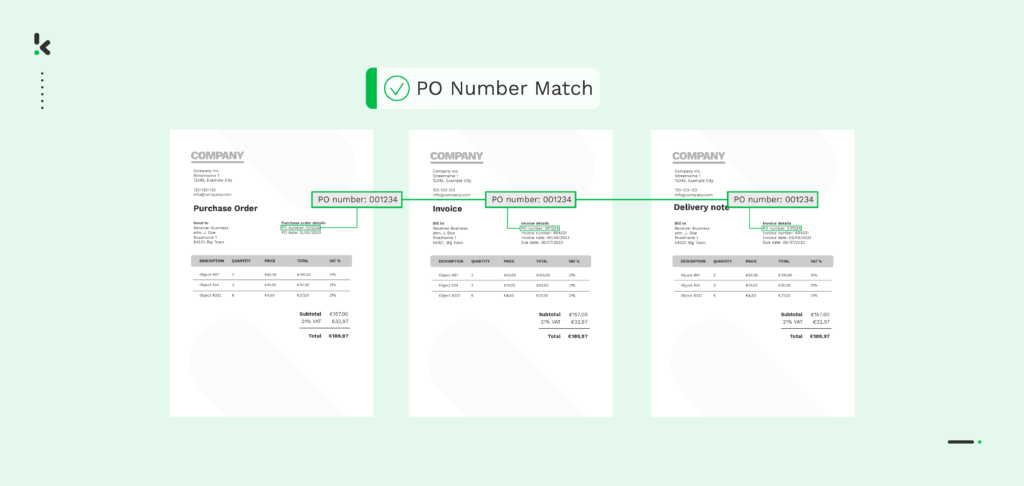
Two/Three-Way Matching
Two and three-way matching in document fraud detection involves cross-referencing information from multiple sources to verify authenticity. For example, with two-way matching, the software can automatically compare invoices with purchase orders to ensure that you’re invoiced only for the items you’ve ordered.
With three-way matching, you add an additional layer of verification by comparing the invoice, purchase order, and proof of delivery. IDP allows you to specify the data fields for comparison, alerting you to matches or discrepancies. It’s crucial for accounts payable, order management, and payment reconciliation, as it helps prevent vendor and invoice fraud.

Manual Fraud Detection vs Automated AI Fraud Detection
In summary, here’s how AI fraud detection measures up against manual verification.
| Manual Document Verification | AI Fraud detection |
Slow and error-prone In the manual verification, an employee who has to review the documentation would need to compare documents item by item or check each line individually. This process can take up a lot of time and is prone to errors. | Fast and accurate processing AI fraud detection solution provides the highest level of accuracy. It helps you to control the quality of your data, leading to more accurate data and better decision-making. |
Slow and error-prone In manual verification, an employee who has to review the documentation would need to compare documents item by item or check each line individually. This process can take up a lot of time and is prone to errors. | Reduced costs With AI-powered solutions, you can greatly reduce the time spent on document verification and, therefore save on overhead costs even at times of document overflow. |
| Low efficiency and engagement Manually verifying fraudulent documents is a tedious process that can cause employee disengagement due to the nature of such repetitive tasks. Instead of using your team’s skills to the fullest, this kind of work wastes the talent your company has. | Increased productivity Using AI fraud detection to handle document verification gives employees more time to focus on tasks that truly matter, resulting in increased productivity and business growth. |
As you can see, a range of technologies has been developed to combat document fraud, and there are numerous providers available to help you effectively address this issue. Klippa DocHorizon, for example, offers a comprehensive solution for document verification. Ready to see how we can assist you? Here’s what we can do for you.
Detect Document Fraud with Automation Through Klippa
Klippa DocHorizon is an advanced Intelligent Document Processing Platform that leverages technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), AI, and Machine Learning to help you combat document fraud and streamline your document workflows.
- Custom Workflows: Create your unique document workflows by simply connecting any relevant DocHorizon modules: data extraction, capture, classification, conversion, anonymization, verification, and more.
- Fraud Detection: Strengthen fraud detection with any of our automated fraud detection modules (we support all of the methods listed above!) for fool-proof & real-time document fraud detection before it causes your business any harm.
- Robust Identity Verification: Enhance security with our comprehensive identity verification module. This includes age verification, selfie verification, liveness detection, and NFC checks to prevent fraud and ensure user identity authenticity.
- Wide Document Support: Process and detect fraud on any document in all Latin alphabet languages or customize data fields for extraction for any use cases.
- Integration Capabilities: Easily integrate our solutions directly on the platform, which supports over 50 data integration options, including cloud solutions, email parsing, CRM, ERP, and accounting software.
- Security & Compliance: Stay compliant and secure by default with Klippa, an ISO 27001 & 9001 certified partner.
Are you ready to see how Klippa’s automated document fraud detection solution can help you? Book a free online demo below or contact one of our experts for more information!
Frequently Asked Questions
Specialized software like document verification tools and AI-based fraud detection platforms such as Klippa DocHorizon can be used to detect fake documents. These tools analyze patterns, compare against databases, and detect inconsistencies.
You can prevent document fraud by using secure document verification solutions like Klippa DocHorizon to validate the documents you are presented with. These can detect fraud in documents more easily than the naked eye can.
You can detect fraud in documents using technology to detect inconsistencies in text formatting, metadata, and signatures, verify their authenticity through databases, and spot alterations and fake credentials.
A common example of document fraud is falsifying pay stubs, identification documents, or certificates, where critical information like numbers or names are altered to deceive.
You can prove document fraud using metadata analysis to detect the presence of alteration software like Photoshop and through cross-verification of documents like bank statements.