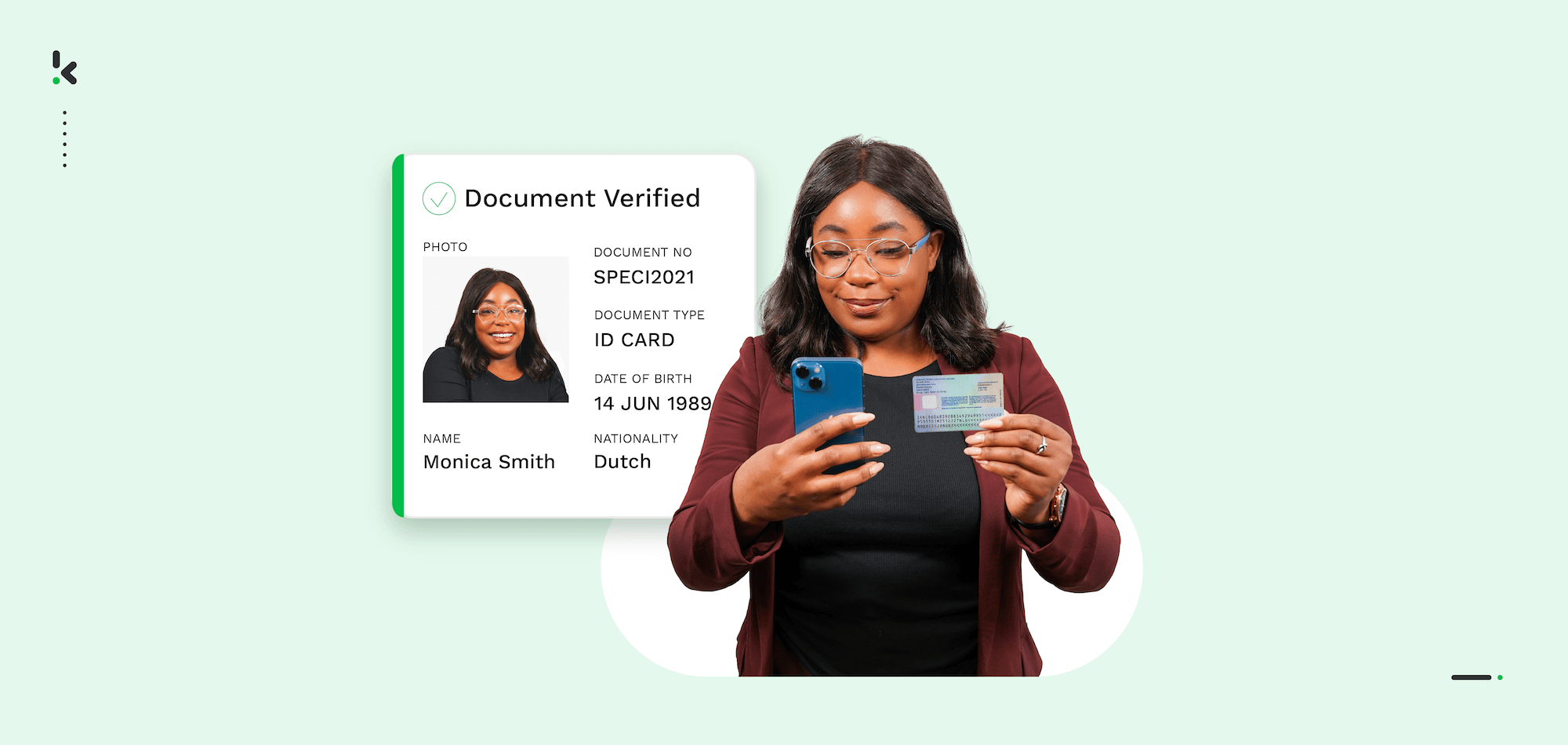

Every year, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) estimates that 2% to 5% of global GDP is laundered – up to €1.87 trillion. Banks face relentless pressure to stop financial crime while staying compliant with evolving Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations.
But traditional, manual Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are slow, error-prone, and frustrating for customers who expect instant digital onboarding. The solution? Using AI, OCR, biometrics, and real-time screening to verify identities in minutes instead of days, cut compliance risk, and enhance the customer experience.
Key Takeaways
- Automating KYC in banking with AI, OCR, biometrics, and real-time screening can cut onboarding time from days to minutes.
- Manual KYC is costly, slow, and error-prone, while automation improves accuracy, scalability, and compliance.
- Core automation steps include identifying bottlenecks, defining risk-based workflows, selecting tools, integrating systems, training staff, and ongoing refinement.
- Banks adopting automated KYC achieve faster onboarding, lower costs, enhanced customer experience, and stronger AML/KYC compliance.
Why Automate KYC in Banking
Manual KYC checks require back-office teams to collect, verify, and process identity documents one by one – a costly, time-consuming approach that struggles to keep pace with high application volumes. The consequences are clear:
- High Costs: Large banks spend tens of millions annually on manual KYC staffing and processing.
- Slow Turnaround: Manual verification can take days, delaying account opening.
- Error Risk: Manual data entry is error-prone, exposing organizations to compliance violations.
- Compliance Pressure: Regulations demand consistent, auditable verification flows.
- Customer Attrition: Long onboarding times lead to abandoned applications, lost revenue, and damaged brand trust.
With automation, banks capture and verify digital ID data in seconds, automatically screen against sanctions and PEP lists, fast-track low-risk customers, and continuously monitor profiles to stay compliant, all at a fraction of the manual cost.
Automation Technologies & Methods for KYC in Banking
Automating KYC checks in banks combines AI, OCR, biometrics, and real-time screening to digitize onboarding, improve compliance, and reduce costs.
Modern KYC automation involves an integrated stack of technologies designed to verify identities faster, more accurately, and with less manual intervention. Here are the core methods used in banking and financial services today:
1. Digital ID & Document Capture (OCR)
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) extracts text and data from passports, driver’s licenses, ID cards, and other official KYC documents.
- Why it matters: Eliminates manual data entry and captures structured information instantly.
- Example: Automatically reading name, date of birth, and expiration date from a scanned passport photo page.
2. AI/ML for Document Validation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) assess document authenticity by checking formats, security features, and visual anomalies.
- Why it matters: Detects expired, altered, or fake IDs in seconds.
- Example: Flagging mismatched font sizes or tampered holograms on a national identity card.
3. Biometric Verification
With biometric verification, facial recognition, voice, or fingerprint scans match a customer to their submitted ID, combined with liveness detection to confirm it’s a real person.
- Why it matters: Prevents identity theft and ensures the person submitting the ID is its rightful owner.
- Example: Matching a selfie to the headshot on a passport and verifying liveness via micro-movements.
4. Automated Sanctions & PEP Screening
Real-time checks against global sanctions databases, Politically Exposed Persons (PEP) lists, and adverse media sources.
- Why it matters: Reduces regulatory risk by preventing the onboarding of high-risk individuals.
- Example: Screening an applicant against OFAC, UN sanctions lists, and country-specific watchlists during onboarding.
5. Risk-Based Routing & Segmentation
Machine learning models score customer risk levels based on identity data and background checks.
- Why it matters: Fast-tracks low-risk clients and flags high-risk cases for manual review.
- Example: Assigning a risk score that moves a low-risk retail banking applicant through a simplified workflow while routing a high-risk applicant to enhanced due diligence.
6. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Automates repetitive operational tasks, such as data intake, profile updates, account status checks, and scheduled compliance reviews.
- Why it matters: Frees employees from routine administration and ensures consistent process execution.
- Example: Auto-updating a customer’s profile when new data from an external registry is received.
7. Perpetual KYC (pKYC) and Ongoing Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of customer profiles and transactions for suspicious changes or activities.
- Why it matters: Detects risk events between periodic reviews, ensuring compliance is maintained year-round.
- Example: Automatically flagging a sudden address change combined with unusual overseas transfers.
Banks integrate these technologies into a seamless workflow, starting with digital ID capture, moving through biometric validation and sanctions screening, then applying risk-based routing, and ending with continuous monitoring. This structure cuts onboarding time from days to minutes while meeting strict AML/KYC regulatory standards.
How to Automate KYC for Banks and Financial Services
Automating KYC involves mapping current bottlenecks, defining digital workflows, selecting the right tools, integrating systems, training staff, and continuously refining processes.
Here’s a practical roadmap banks can apply:
Step 1: Identify Bottlenecks in Your Current KYC Process
Map out your customer onboarding journey from application submission to account activation.
- Look for: Long document verification times, multiple data entry points, high error rates, and redundant manual checks.
- Example: Discovering that proof-of-address checks take 48 hours due to manual database queries.
Step 2: Define Automated Workflows by Risk Level
Design KYC processes that automatically adjust based on customer risk scoring.
- Low-risk: Straight-through processing with minimal friction.
- High-risk: Enhanced due diligence with additional verification layers.
- Example: Routing a standard retail account to simplified KYC, while routing a politically exposed person (PEP) to full investigation.
Step 3: Select the Right Automation Tools
Choose platforms that cover the essential KYC automation capabilities: OCR, AI/ML validation, biometric verification, sanctions screening, RPA, and pKYC monitoring.
- Tip: Ensure tools meet AML/KYC compliance standards and can handle your document types and languages.
- Example: Selecting an OCR engine trained on passports and IDs from all supported countries and integrating with global sanctions lists.
Step 4: Integrate Automation Into Core Banking Systems
Connect your automation tools with CRM, CLM, payment gateways, and compliance databases to create a seamless workflow.
- Tip: Use APIs or middleware to reduce integration time and allow real-time data syncing.
- Example: Biometric verification results update the CRM instantly, triggering account activation.
Step 5: Train Staff to Manage and Oversee the System
Ensure employees know how to operate the tools, handle flagged cases, and troubleshoot common issues.
- Tip: Provide scenario-based training for compliance officers so they can make fast, informed decisions on escalations.
- Example: Training staff to differentiate between genuine watchlist hits and false positives.
Step 6: Maintain and Iterate for Evolving Risks
Schedule regular reviews of KYC automation performance and update workflows for new regulations or fraud patterns.
- Tip: Use feedback loops from compliance audits to fine-tune risk scoring and improve accuracy.
- Example: Updating the ML model to detect newly popular forged ID templates.
By following this roadmap, banks can roll out automation in a controlled, regulation-ready fashion. The result is faster onboarding (minutes instead of days), fewer errors, lower costs, and a friction-free experience for both customers and compliance officers.
Key Benefits of Automated KYC for Banks
Automated KYC replaces manual identity checks with fast, tech-driven workflows, cutting onboarding time, reducing costs, and improving compliance.
By implementing automation with AI, OCR, biometrics, and real-time screening, banks unlock significant operational and customer experience advantages:
Faster Onboarding
- Impact: Reduce verification times from days to minutes.
- Result: Customers can open accounts or access services almost instantly.
- Example: An online bank cuts average account opening from 48 hours to under 5 minutes.
Lower Operational Costs
- Impact: Eliminate manual data entry and reduce compliance headcount needs.
- Result: Up to 90% reduction in KYC processing costs.
- Example: Automating ID checks saves thousands of manual hours annually.
Improved Accuracy
- Impact: Reduce human-input error rate (~1%) to near zero with machine validation.
- Result: Higher data integrity and fewer false positives/negatives in screening.
- Example: OCR and AI detect and flag forged IDs before onboarding completes.
Enhanced Compliance
- Impact: Consistent AML/KYC adherence with audit trails and policy enforcement.
- Result: Lower risk of regulatory fines or sanctions.
- Example: Automatic checks against sanctions lists ensure no high-risk entities slip through.
Better Customer Experience
- Impact: Smooth, mobile-friendly onboarding without repeated document requests.
- Result: Higher conversion rates and customer loyalty.
- Example: Retail customers in emerging markets open accounts directly from smartphones using biometric liveness checks.
Scalability for Growth
- Impact: Handle high application volumes without scaling staff proportionally.
- Result: Support expansion into new geographies and service lines.
- Example: A regional bank grows into three new markets without increasing KYC staff.
Continuous Monitoring (pKYC)
- Impact: Detect risks between periodic reviews by tracking changes over time.
- Result: Proactive risk reduction and faster intervention during suspicious activity.
- Example: System flags address change + unusual overseas transactions within hours.
Automated KYC offers banks a triple win: faster onboarding, stronger compliance, and lower costs, while meeting the digital expectations of modern customers.
Automating KYC with Klippa DocHorizon: Case Study – Online Payment Platform (OPP)

One of the Netherlands’ leading online payment providers, Online Payment Platform (OPP), serves over 5 million users worldwide, facilitating secure customer-to-customer transactions in online marketplaces.
The Challenge
With the scale of their operations, verifying identity documents was crucial to fraud prevention. However, OPP faced multiple bottlenecks:
- Manual identity checks could take up to 24 hours, delaying payment approvals.
- Human error in KYC verification increased vulnerability to document fraud.
- Resource-heavy workflows meant two full-time back-office employees spent their days manually reviewing IDs.
- Inaccurate checks risked identity theft.
The need for a faster, more reliable, and scalable identity verification process became urgent.
The Solution
OPP chose Klippa DocHorizon to automate its KYC document verification, leveraging:
- OCR with Global Coverage – Able to process IDs from any country.
- MRZ (Machine Readable Zone) Checks – Enhanced passport & ID authenticity verification.
- Data Extraction Accuracy – Up to 99% accurate parsing of fields like name, date of birth, and document number.
- Versatile Document Support – Beyond IDs, Klippa could process salary slips, proof of income, and other verification documents.
- Document Fraud Detection – Prevents identity document fraud by identifying forgery with AI.
Automated KYC Process in Action
- User Uploads Documents – After placing an order, users submit IDs via the platform.
- OCR Processing – Klippa’s OCR instantly reads and extracts all relevant data from the document.
- MRZ Validation – For passports and IDs, MRZ checks confirm authenticity.
- Cross-Check Data – Extracted data is matched against the user’s input for consistency.
- Automated Approval – Valid documents are approved automatically, eliminating manual review delays.
The Impact
With Klippa DocHorizon:
- Processing Speed – Reduced from 24 hours to seconds.
- Volume Handling – Over 300K identity documents processed monthly without additional staff.
- Manual Lift Removed – Freed back-office employees from repetitive, error-prone checks.
- Fraud Prevention – High-precision verification keeps fraudulent documents out of the system.
- Customer Experience – Faster onboarding and transaction approvals improve user satisfaction.
While OPP operates in the online payment space, the same workflow applies to any bank or financial institution:
- Replace manual KYC checks with automated OCR + AI verification.
- Expand coverage to handle global document types.
- Cut costs, improve accuracy, and stay fully AML/KYC compliant.
Ready to automate your KYC checks? Book a Demo today to see how Klippa can cut your KYC onboarding times from days to minutes.
FAQ
KYC stands for Know Your Customer, a process that banks use to verify the identity of their customers. This ensures compliance with regulations and helps prevent fraud, money laundering, and other financial crimes.
KYC is critical because it helps banks identify their customers, assess risks, and comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. It also safeguards the financial system from illegal activities and protects the bank’s reputation.
Typically, banks require proof of identity, such as a passport or driver’s license, and proof of address, like a utility bill or bank statement. These documents help verify the customer’s identity and residence.
KYC automation uses technologies like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to scan, extract, validate, and store customer data. This streamlines the onboarding process, reduces human error, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.