
AI technologies are here to stay and are making their mark on our daily lives. From the playlists recommended by your streaming app to the photos your phone organizes automatically, AI works quietly behind the scenes to make life easier.
The same is true for images. AI-based image processing is helping businesses around the world speed up tasks that used to take hours. Whether it’s scanning documents, verifying IDs, or pulling information from receipts, AI makes it faster, smarter, and a lot less manual.
In this guide, we’ll break down what AI image processing is, how it works, where it’s used, and how it can help you automate your document and image workflows.
Key Takeaways
- AI image processing automates visual and document tasks. It speeds up processes like document classification, data extraction, and image recognition.
- It combines AI technologies to analyze and understand images. Deep learning, OCR, and NLP work together to process both images and scanned documents.
- Organizations in nearly every industry use AI image processing. Banking, healthcare, retail, legal, and many others rely on it to reduce manual work and improve accuracy.
- Platforms like Klippa DocHorizon simplify document workflows. They offer secure, customizable solutions for extraction, verification, and fraud prevention.
What is AI Image Processing?
AI image processing uses artificial intelligence to help computers understand and work with images. It allows systems to detect patterns, recognize objects, improve image quality, and even extract useful information from pictures or documents.
The main goal is to automate tasks that would normally require human vision and decision-making. For example, AI can sort photos, read text from scanned papers, detect faces, or highlight objects in security footage.
At the heart of AI image processing are models trained to analyze images. These models can identify shapes, colors, and textures to understand what they are looking at. As a result, businesses and industries can process large amounts of visual data quickly and with high accuracy.
Types of AI Image Processing
Image Recognition and Classification
This involves training AI models to recognize and categorize objects within images and can be applied to include facial recognition, object detection, and image categorization.
Image Segmentation
This involves dividing an image into segments to analyze specific regions independently.
Image Enhancement
Utilizes AI algorithms to improve the quality of images by reducing noise, adjusting brightness and contrast, and enhancing sharpness.
Forgery Detection
Focuses on identifying inconsistencies and irregularities in images, commonly applied in tasks like spotting fake IDs or document fraud
Image Retrieval
Utilizes AI to browse and search images from a large database of digital images that are similar to an original image.

How Does AI Image Processing Work?
Here’s how the process works step by step.
Step 1. Data Collection
The first step is gathering a large set of labeled images that match the task. For example, a facial recognition model would use photos of faces with labels showing the identity of each person.
Step 2. Pattern Recognition
The AI model begins to study the images and spot patterns. It looks for shapes, textures, and features that help it understand what it is seeing.
Step 3. Model Training
A deep learning model, often a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), is trained on the dataset. It learns to associate specific patterns with specific outcomes, like recognizing the unique features of different faces.
Step 4. Feature Extraction
The trained model can now detect key details in new images. In facial recognition, for example, it might focus on the distance between the eyes or the shape of the mouth.
Step 5. Validation and Fine-Tuning
The model is tested on new images to check accuracy and avoid overfitting. Overfitting happens when the model performs well on training data but struggles with new, unseen images.
Step 6. Inference
At this stage, the AI is ready to work with real-world images. It uses what it has learned to make predictions or decisions, like matching a photo to a person in a database.
Step 7. Post-Processing and Visualization
The system refines its output and can present the results in a way that’s easy to understand.
Step 8. Continuous Learning
Even after deployment, AI models keep improving. They are retrained with fresh data and user feedback to stay accurate and reliable over time.
This may be all very abstract to understand, so let’s break it down into some practical applications of AI image processing.
Applications of AI in Image Processing
AI in image processing has practical uses across many industries. Here are some of the most common examples.
Image Enhancement in Photography and Video Editing
AI tools can automatically clean up photos and videos. They remove unwanted noise, fix poor lighting, sharpen blurry images, and enhance colors to create clearer and more attractive visuals. This is widely used in smartphone cameras, editing software, and even medical imaging to improve scan quality.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition uses AI to analyze the unique features of a person’s face and match it to a stored profile. It is used for security and identity verification, such as unlocking smartphones, monitoring restricted areas, or tagging people in photos on social media. Businesses also use it to track attendance or customer footfall.
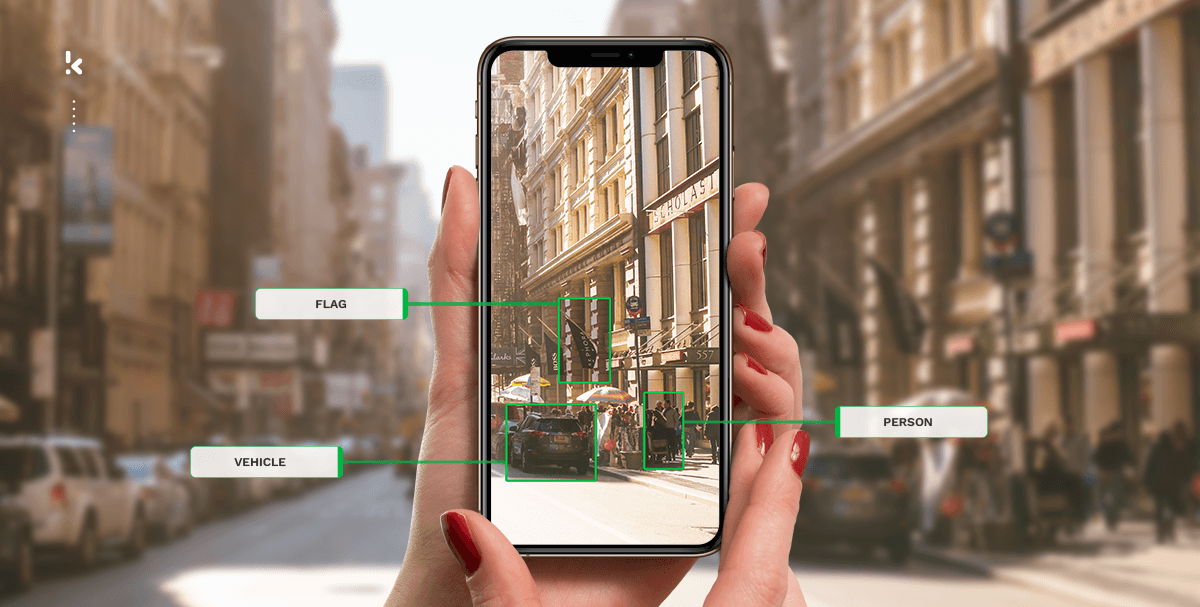
Object Detection
AI can scan images or videos and detect objects such as cars, street signs, animals, or products. This is critical in industries like transportation and logistics. For example, self-driving cars rely on object detection to understand their surroundings and make driving decisions.
Reverse Image Search
With reverse image search, AI compares a picture to massive databases of images to find duplicates or similar versions. It helps users track down the source of a photo, check for copyright issues, or find products and information based on a visual search.
These examples are just the beginning. This technology is also used in healthcare to help diagnose diseases from scans, in agriculture to monitor crop health, and in retail to manage inventory and improve the online shopping experience.
The following sections will explore some practical uses of AI-based image processing in document-centric workflows.
AI Image Processing in Document Workflows
AI image processing plays a key role in making document-heavy processes faster and more accurate. It helps organizations reduce manual work and minimize human error.
The process usually starts when documents are captured, either by scanning paper files or uploading digital images. AI then cleans up the image by adjusting contrast, removing shadows, or straightening the text for easier reading.
One of the most common uses is in combination with Optical Character Recognition (OCR). OCR technology recognizes text from images and converts it into machine-readable formats. AI improves OCR by handling poor-quality scans or unusual layouts more effectively.
AI can also classify documents by type, detect important fields like names or invoice numbers, and extract specific information from contracts, forms, or receipts. It uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand the context of the data, helping businesses automate approval workflows, data entry, and filing tasks.
Validation checks are built in to ensure accuracy, and the processed data can be integrated directly into business systems for faster reporting or compliance tracking.
The end result is a streamlined document management process where information is easier to search, store, and use.
Note: If you are curious how popular LLMs, like Chat GPT, Claude, and DeepSeek, handle document processing, read our guide here.
Now that we’ve seen how AI supports document workflows, let’s take a closer look at what happens behind the scenes. Here’s how AI-based image processing software works to automate document tasks step by step.
How AI Image Processing Software Works in Document Automation
AI image processing software can automate document-heavy workflows that would normally require hours of manual work. Let’s take the example of invoice processing to explain how it works.
- Input: The process starts by feeding the system with a scanned document or image, such as an invoice. This image might contain both text and visual elements. Some companies use mobile scanning SDKs or apps to capture documents in real-time.
- Preprocessing: The software cleans up the image to get it ready for analysis. It may adjust brightness and contrast, remove background noise, crop edges, or straighten tilted scans to improve accuracy.
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition): Next, the software uses OCR to recognize and extract text from the image. For an invoice, this could mean pulling out key details like merchant names, dates, line items, totals, and taxes.
- Text Extraction and Interpretation: AI goes beyond just recognizing text. It also understands relationships between data using natural language processing (NLP). For example, it can match a price to the correct product name or identify a payment due date.
- Machine Learning Adaptation: Invoices and documents come in many formats. Machine learning allows the software to adapt to different layouts and document types by learning from previous examples, improving over time.
- Verification: The system double-checks the extracted data for accuracy. It can cross-reference information with databases or perform two-way matching to identify missing or conflicting data.
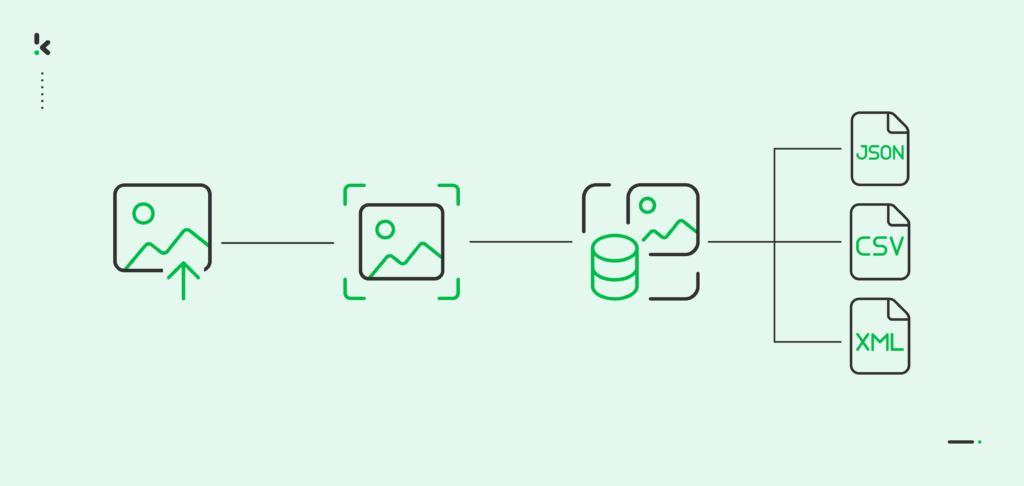
- Data Structuring and Export: The final step is turning the extracted information into structured formats like JSON, CSV, or XML. This allows the data to be integrated directly into accounting, ERP, or document management systems.
This example shows how AI image processing software reduces errors, saves time, and creates smoother document workflows for businesses.
Benefits of Implementing AI in Image Processing
Using AI to process images offers clear advantages for businesses and organizations that work with large volumes of images or documents.
- Streamlines Processes: AI can handle tasks that used to require hours of manual effort. It automates repetitive jobs like sorting images, reading scanned documents, or verifying identity documents, which helps teams focus on more valuable work.
- Improves Accuracy: AI-powered systems can detect small details and patterns that humans might miss. This leads to fewer errors in document processing, image analysis, or data extraction.
- Reduces Costs: By automating manual tasks, companies can cut down on labor costs and reduce the need for expensive manual quality checks.
- Increases Productivity: Teams can process large numbers of documents or images quickly, which boosts overall productivity and shortens turnaround times.
- Supports Better Decision-Making: AI helps organizations access accurate and structured data faster. This makes it easier to analyze information, spot trends, and make informed decisions.
- Scales Easily: Once trained, AI models can handle increasing amounts of work without the need for extra resources. This makes it easy for businesses to grow their operations.
As impressive as these benefits are, it’s important to be aware of the challenges that can come with using AI in image processing. Let’s take a closer look.
Challenges and Considerations
While this technology offers major benefits, there are also challenges to think about before implementing it in your workflows.
- Data Privacy and Security: AI systems often work with sensitive data like personal documents or identification photos. It is essential to protect this information and comply with privacy regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- High-Quality Training Data: AI models rely on large sets of labeled images for training. Poor-quality or limited data can lead to inaccurate results. Gathering and preparing the right data can be time-consuming and costly.
- Complex Integration: Adding AI to existing systems may require changes to infrastructure or processes. It’s important to have a clear plan and the right technical expertise to ensure smooth integration.
- Bias and Fairness: If the data used to train an AI system is biased, the results will be too. This can lead to unfair or inaccurate outcomes. Regular monitoring and retraining are key to maintaining fairness and accuracy.
- Ongoing Maintenance: AI models are not “set and forget.” They need regular updates and fine-tuning to adapt to new types of data, changes in workflows, or updated business needs.
Understanding these challenges can help you plan ahead and make the most of what AI image processing has to offer.
Industry Use Cases for AI Image Processing
Organizations of all sizes use this technology to automate tasks, reduce errors, and improve operational efficiency. Here are some of the most common examples across industries:
Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics use AI to extract patient details from medical records, insurance documents, and test results. This speeds up administrative tasks, reduces paperwork, and helps healthcare providers focus on patient care.
Recruitment and Human Resources
AI can parse resumes and applications to pull out candidate details such as names, contact information, skills, education, certifications, and experience. This helps recruiters and HR teams quickly shortlist qualified applicants and improve hiring processes.
Retail and E-Commerce
AI-powered scanning solutions can capture information from price tags, product labels, and barcodes. Retailers use this data for inventory management, price verification, and improving shelf accuracy in stores.
Banking and Finance
Financial institutions rely on AI image processing to automate the handling of large volumes of documents, including invoices, bank statements, receipts, payslips, and purchase orders. This minimizes manual data entry and reduces errors in accounting and compliance workflows.
Legal and Compliance
Law firms and corporate legal departments use AI to analyze contracts and legal documents. AI can automatically extract clauses, deadlines, obligations, and key terms, helping legal teams speed up document review and reduce human error.
Identity Verification
AI systems can scan and verify details from passports, driver’s licenses, national ID cards, and other identity documents. Industries such as banking, travel, and telecommunications use this technology to meet regulatory compliance and prevent fraud.
AI image processing allows companies across these sectors to cut manual work, lower costs, and manage larger volumes of documents and visual data with greater speed and accuracy.
We’ve covered what AI image processing is, how it works, and the ways it’s helping businesses across industries simplify complex tasks. So, how can your organization start using this technology to improve document workflows and reduce manual work? The next step is exploring intelligent document processing solutions like Klippa DocHorizon.
How to Get Started with AI-based Image Processing?
The first step to adopting AI image processing is to review where it can add the most value. Look at workflows that involve repetitive document handling, manual data entry, or slow visual checks. These are often the best places to start.
When exploring solutions, consider platforms that offer strong data extraction capabilities, flexibility to handle different document types, and seamless integration with your existing systems. Pay close attention to security features and compliance with privacy regulations to ensure your data stays protected.
If you’re ready to take the next step, Klippa offers an intelligent document processing solution designed to automate document workflows at scale. Our platform uses AI-driven image processing for document extraction, conversion, classification, anonymization, and fraud prevention.
To see how Klippa DocHorizon can fit your needs, visit our flow builder page or book a demo with one of our experts today.
FAQ
Traditional image processing follows fixed rules to enhance images or detect shapes. AI image processing uses machine learning to learn from data, making it better at complex tasks like object detection, text extraction, and pattern recognition.
Yes. AI-powered handwriting recognition can extract data from handwritten forms, notes, or scanned documents. Accuracy depends on handwriting quality and the system’s training, but has improved significantly in recent years.
In many cases, AI document extraction can reach over 90% accuracy. Results depend on document quality and data type. Many systems use a human-in-the-loop approach, where human checks are added at key steps to further improve accuracy and catch any errors the AI might miss.
Yes, if designed properly. Tools like Klippa DocHorizon offer features like encryption, data anonymization, secure hosting, and GDPR compliance to protect sensitive documents.
Almost any industry that works with large amounts of documents, images, or visual data can benefit. Common sectors include banking, healthcare, legal, retail, logistics, insurance, and HR. But AI is also being adopted in education, government, real estate, manufacturing, and more to automate tasks, reduce errors, and speed up data handling.